
 Apr 28,2025
Apr 28,2025
 Reunion
Reunion
Batteries have become an indispensable part of modern life, powering everything from TV remotes to electric vehicles.
At their core, batteries are electrochemical devices that convert chemical energy into electricity. Several battery types dominate the market, each with its own strengths and weaknesses, including lithium-ion (Li-ion), nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), and lead-acid. Ubiquitous in today’s digital world, rechargeable Li-ion batteries power laptops, smartphones, and tablets, offering high energy density and long lifespans. Although they have a lower energy density than Li-ion batteries, NiMH batteries are known for their environmental friendliness and wide operating temperature range. Lead-acid batteries are the workhorses of the automotive industry, used in traditional gasoline-powered vehicles to start the engine and store electrical energy. They are reliable and relatively inexpensive, but bulky and heavy. Alkaline, the most common disposable battery, and compact coin cell batteries, also referred to as button cells, predominantly serve the consumer market where low-drain, lifespan or size are a priority.
The Rise of New Technologies: Powering the Future
Next-generation Li-ion: Research on existing lithium-ion battery technology continues apace, including developing higher-capacity anode and cathode materials to store more energy and extending lifespans to reduce replacement.
Lithium-Titanate-Oxide (LTO): This rechargeable battery uses lithium-titanate nanocrystals rather than carbon, reducing thermal runaway and overheating while offering longer cycle counts compared to a traditional lithium battery.
Solid-state: Potentially safer, faster charging, with a longer lifespan than conventional Li-ion batteries, they are still under development and not yet commercially available.
Lithium-sulfur (Li-S): These batteries boast a much higher theoretical energy density than Li-ion batteries and could potentially provide significantly longer driving ranges for EVs. Notable challenges remain, however, in the management of their lifespans (poor cycle life) and internal resistance.
Redox Flow: These large-scale storage solutions are designed for applications like grid energy storage and powering entire buildings, offering scalability and long lifespans.
Organic: This broad category of batteries uses organic materials as electrodes or electrolytes. While organic batteries are potentially safer and more environmentally friendly than traditional options, research is still in its early stages.
Battery storage systems, also referred to as battery energy storage systems (BESS), are essentially large rechargeable batteries that store electrical energy. They work by converting electrical energy into chemical energy during charging and then reversing the process to release the stored energy back as electricity when needed.
As the world transitions towards a more sustainable energy future, battery energy storage systems are becoming increasingly important. Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are intermittent, i.e., solar panels only generate electricity during sunny daylight hours and wind turbines only generate electricity when the wind is blowing. Battery storage systems help to regulate these fluctuations by storing excess energy when it is generated so it is available when it is needed.
Battery storage systems can provide backup power in the event of a power outage. Additionally, they may be used to help reduce “peak demand” costs that businesses and homeowners see on their utility bills. By storing energy during off-peak hours and releasing it when demand is high, battery energy storage systems help reduce the overall amount of electricity that needs to be drawn from the grid at peak times.
While batteries themselves store the energy, connectors play a vital role in establishing a reliable and secure electrical connection between the battery and the device it powers. Connectors act as the bridge between various parts, performing several key functions:
Connector options commonly used with various battery types
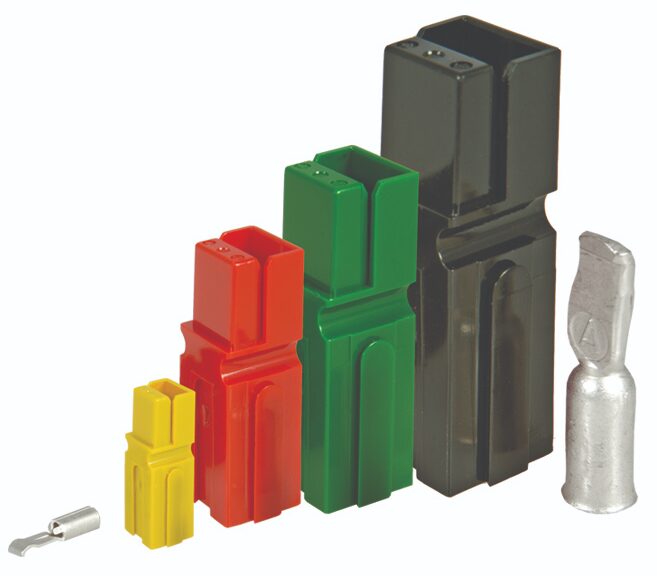
Anderson Power Products (APP) specializes in high-power connectors designed for heavy-duty applications. Its SB series connectors are popular for their large current carrying capacity and secure locking mechanism, They are ideal for connecting large battery packs to electric vehicle motors or industrial machinery. APP’s Powerpole and multipoles are high quality solutions from the battery to charging outlets. Their SBS50 is designed to work with lead acid, while the SBS75X is designed with signaling capabilities for Li-ion monitoring.

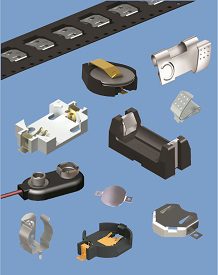
Keystone Electronics offers a wide range of battery holders that come with pre-attached connectors. These connectors can be screw terminals, solder terminals, or even specialized connectors for specific battery types. There are virtually as many battery holders, retainers, contacts, clips, straps, and snaps as there are cell or battery configurations. Most configurations today are designed so that the batteries can be quickly and easily installed and replaced. Many are available on tape-and-reel in addition to loose pieces.
Mill-Max’s spring-loaded pins are a perfect solution for charging batteries in portable instruments and docking handheld devices for data and power transfer purposes. They can be easily integrated into any system with numerous options available in terms of height, travel, and spring force. The new Omniball spring-loaded connectors for applications requiring multiple points of contact in sliding or rotational orientations. The unique Omniball spring-loaded features a rolling ball interface, enabling contact to be made between components in axial and non-axial alignments.

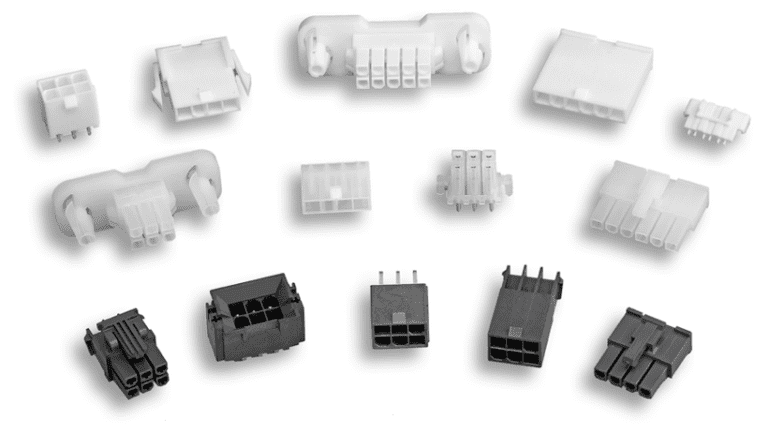
Molex’s Mini-Fit series of connectors can be suitable for connecting smaller rechargeable batteries to PCBs in some electronic devices due to their compact size and reliable connection. While many applications will require a custom-designed battery connector, Molex is able to offer various battery connectors as standard products, with configurations including SMT, compression-style, and through-hole interfaces to the PCB; different circuit sizes; right-angle or parallel battery pack PCB orientations; and different pitch sizes.
Phoenix Contact offers a robust selection of terminal blocks and power connectors suitable for high-current applications, including screw-clamp terminal blocks commonly used for connecting large lead-acid batteries or other high-power batteries to industrial equipment and connectors and cable assemblies used in utility grade storage. Utility installations for energy storage are made up of batteries in racks, put into modules and ganged together to produce significant power. These modules can be linked in a series or stand alone as a single unit. On the front, each module has connectivity to a management system that goes from module to module.

Choosing the right connector depends on several factors, including the battery type, voltage, current rating, and desired connection method (soldering, screwing, etc.). Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for both the battery and the connector to ensure a safe and compatible electrical connection, or work with a trusted outside resource to help in the design process.
REUNION can design special connectors and cable assembly for photovoltaics, wind power, solar energy, energy storage, inverters, electric vehicles, electric bicycles, charging piles and other fields.
Copyright © Shenzhen Reunion Electronics Co., Ltd.
